seata实现分布式事务
一、Seata简介
Seata 是一款开源的分布式事务解决方案,致力于提供高性能和简单易用的分布式事务服务。Seata 将为用户提供了 AT、TCC、SAGA 和 XA 事务模式。
在Seata中,一个AT分布式事务的生命周期如下:
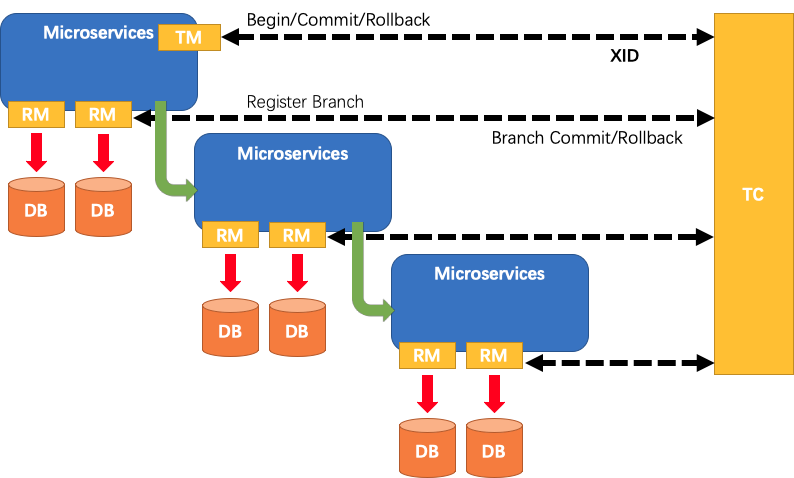
- TM请求TC开启一个全局事务,TC会生成一个XID作为该全局事务的编号,XID会在微服务的调用链路中传播,保证将多个微服务的子事务关联在一起
- RM请求TC将本地事务注册为全局事务的分支事务,通过全局事务的XID进行关联
- TM请求TC告诉XID对应的全局事务是进行提交还是回滚
- TC驱动RM将XID对应的自己的本地事务进行提交还是回滚
二、Seata AT事务
使用前提:需要分布式事务的系统必须是自己可掌控的【因为需要添加数据表】
AT事务时基于两阶段提交XA协议的演变【并没使用XA协议,参考XA协议自定义了一种业务层的规则】
一阶段:业务数据和回滚日志记录在同一个本地事务中提交,释放本地锁和连接资源
二阶段:异步化提交,非常快速地完成。发生错误时回滚通过一阶段的回滚日志进行反向补偿
写隔离机制
- 一阶段本地事务提交前,需要确保先拿到
全局锁。 - 拿不到
全局锁,不能提交本地事务。 - 拿
全局锁的尝试被限制在一定范围内,超出范围将放弃,并回滚本地事务,释放本地锁。
举例说明
两个全局事务tx1和tx2,分别对a表的m字段进行更新操作,m的初始值1000
①、tx1先开始,开启本地事务,拿到本地锁,更新操作m = 1000 - 100 = 900。本地事务提交前,先拿到该记录的全局锁,本地提交释放本地锁。
②、tx2后开始,开启本地事务,拿到本地锁,更新操作m = 900 - 100 = 800。本地事务提交前,尝试拿该记录的全局锁 ,tx1全局提交前,该记录的全局锁被tx1持有,tx2需要重试等待全局锁
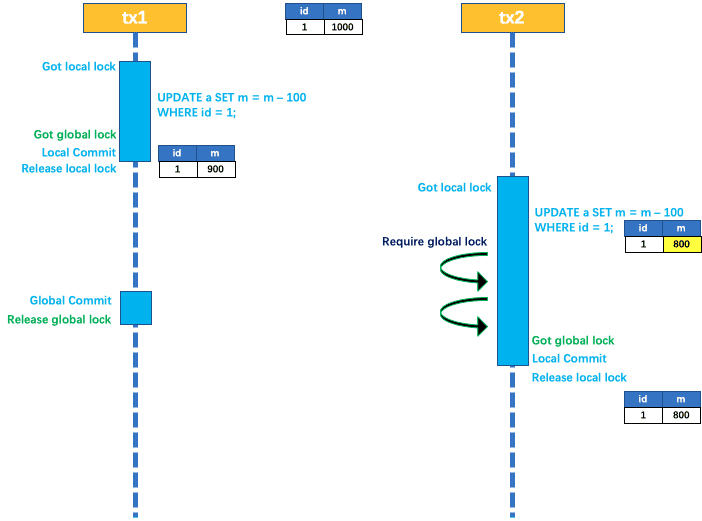
③、tx1二阶段全局提交释放全局锁 。tx2拿到全局锁提交本地事务。
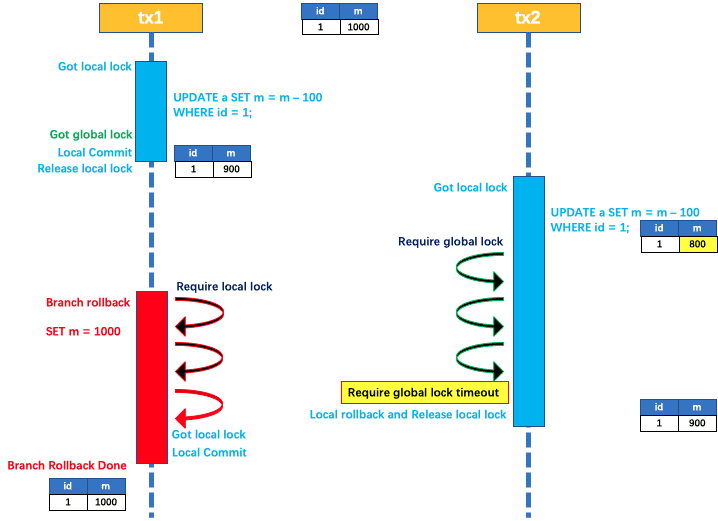
如果tx1的二阶段全局回滚,则tx1需要重新获取该数据的本地锁,进行反向补偿的更新操作实现分支的回滚。此时,如果tx2仍在等待该数据的全局锁,同时持有本地锁,则tx1的分支回滚会失败。分支的回滚会一直重试,直到 tx2 的全局锁等锁超时,放弃全局锁并回滚本地事务释放本地锁,tx1的分支回滚最终成功。
因为整个过程全局锁在tx1结束前一直是被tx1持有的,所以不会发生脏写的问题
读隔离机制
在数据库本地事务隔离级别读已提交(Read Committed)或以上的基础上,Seata(AT 模式)的默认全局隔离级别是读未提交(Read Uncommitted)
如果应用在特定场景下,必需要求全局的读已提交,目前Seata的方式是通过”SELECT FOR UPDATE”语句的代理
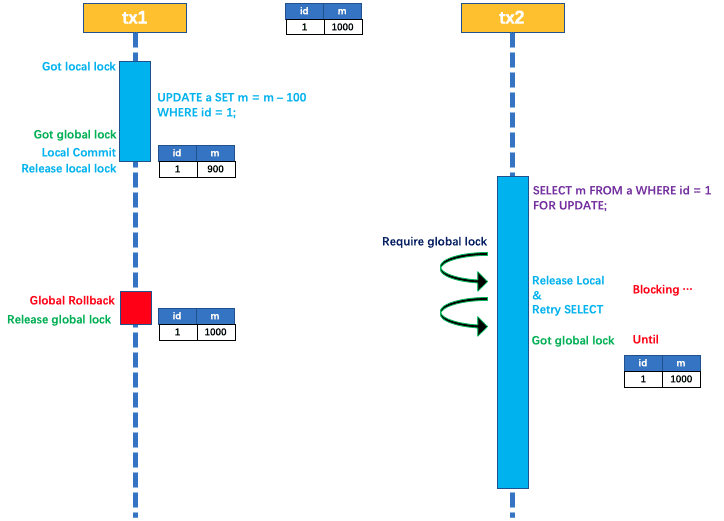
SELECT FOR UPDATE 语句的执行前会申请全局锁,如果全局锁被其他事务持有,则释放本地锁(回滚 SELECT FOR UPDATE语句的本地执行)并重试。这个过程中,查询是被 block 住的直到全局锁拿到,即读取的相关数据是已提交的,才返回。
出于总体性能上的考虑,Seata目前的方案并没有对所有SELECT语句都进行代理,仅针对FOR UPDATE的SELECT语句
工作机制
一阶段:在一阶段,Seata 会拦截业务SQL,首先解析SQL语义找到业务SQL要更新的业务数据,在业务数据被更新前,将其保成”before image”,然后执行业务SQL更新业务数据,在业务数据更新之后再将其保存成”after image”,最后生成行锁。以上操作全部在一个数据库事务内完成,这样保证了一阶段操作的原子性。
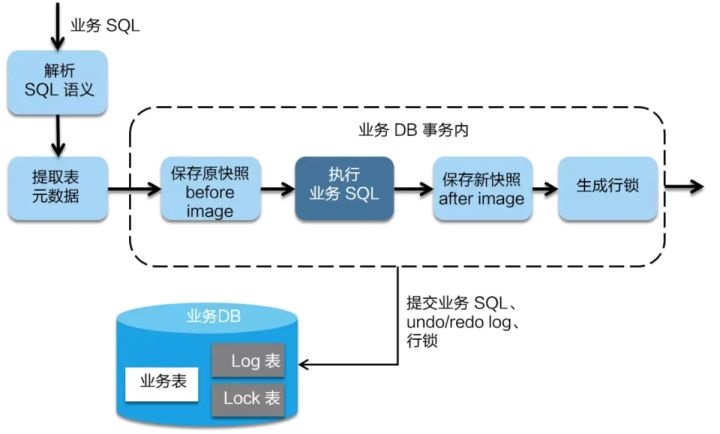
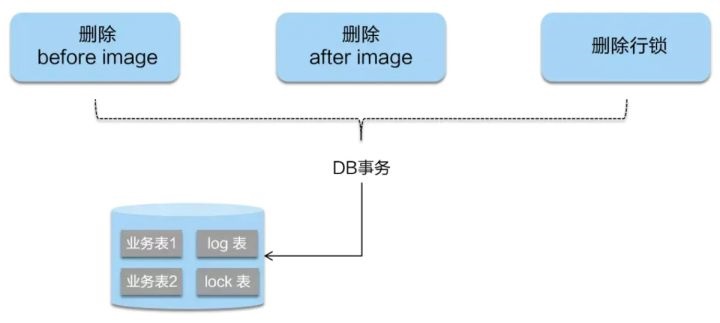
二阶段提交: 二阶段如果是提交的话,因为业务 SQL在一阶段已经提交至数据库, 所以Seata框架只需将一阶段保存的快照数据和行锁删掉,完成数据清理即可。
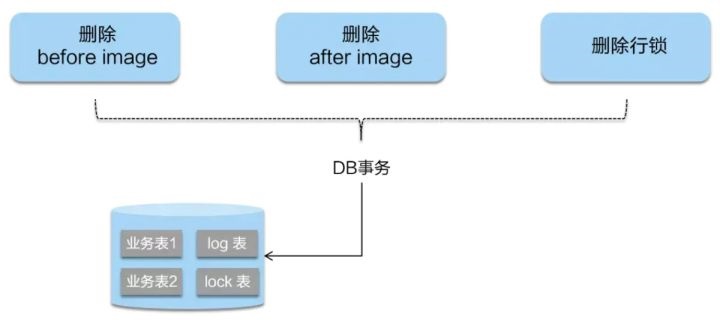
二阶段回滚:二阶段如果是回滚的话,Seata就需要回滚一阶段已经执行的业务SQL,还原业务数据。回滚方式便是用”before image”还原业务数据;但在还原前要首先要校验脏写,对比数据库当前业务数据和”after image”,如果两份数据完全一致就说明没有脏写,可以还原业务数据,如果不一致就说明有脏写,出现脏写就需要转人工处理。
代码示例
前置步骤:选择script\client\at\db的对应数据库脚本执行生成undo_log表
订单服务
@Override
@GlobalTransactional //seata全局事务注解
public String createOrder(Integer userId, Integer productId) {
Integer amount = 1; // 购买数量,暂时设为 1
log.info("[createOrder] 当前 XID: {}", RootContext.getXID());
// 减库存 (feign的调用) http远程调用
Store store = feignProductService.reduceStock(productId, amount);
// 减余额
feignAccountService.reduceBalance(userId, store.getPrice().toPlainString());
// 下订单
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(userId);
order.setProductId(productId);
order.setPayAmount(store.getPrice().multiply(new BigDecimal(amount)));
orderMapper.insertSelective(order);
log.info("[createOrder] 下订单: {}", order.getId());
//int a = 10 / 0;
// 返回订单编号
return String.valueOf(order.getId());
}
仓储服务
@Slf4j
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class StoreServiceImpl implements StoreService {
private final StoreMapper storeMapper;
@Override
public Store reduceStock(Integer productId, Integer amount) {
log.info("[reduceStock] 当前 XID: {}", RootContext.getXID());
// 检查库存
Store store = storeMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(productId);
if (store.getStock() < amount) {
throw new RuntimeException("库存不足");
}
// 减库存
int updateCount = storeMapper.reduceStock(productId, amount);
// 减库存失败
if (updateCount == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("库存不足");
}
// 减库存成功
log.info("减库存 {} 库存成功", productId);
return store;
}
}
账户服务
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private final AccountMapper accountMapper;
@Override
public void reduceBalance(Integer userId, BigDecimal money) {
log.info("[reduceBalance] 当前 XID: {}", RootContext.getXID());
// 检查余额
Account account = accountMapper.selectAccountByUserId(userId);
if (account.getBalance().compareTo(money) < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足");
}
// 扣除余额
int updateCount = accountMapper.reduceBalance(userId, money);
// 扣除成功
if (updateCount == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足");
}
log.info("[reduceBalance] 扣除用户 {} 余额成功", userId);
}
}
上述所有服务的YAML配置
seata:
# Seata应用编号,默认为${spring.application.name}
application-id: ${spring.application.name}
enabled: true
# 注册中心
registry:
type: nacos
nacos:
cluster: SEATA
server-addr: localhost
namespace: DEV
# Seata事务组编号,用于TC集群名
tx-service-group: ${spring.application.name}-group
# 虚拟组和分组的映射
service:
vgroup-mapping:
# 此配置需要和seata中register文件的cluster一致
seata-at-order-service-group: 'SEATA'
feign:
client:
config:
default:
logger-level: FULL
read-timeout: 5000
connection-timeout: 5000
在可能出现并发问题但不是分布式事务的服务,比如上述例子有修改库存的服务,可能会导致数据脏写需要加
@GlobalLock注解
三、Seata TCC事务
AT模式基本上能满足我们使用分布式事务大部分需求,但涉及非关系型数据库与中间件的操作、跨公司服务的调用、跨语言的应用调用就需要结合TCC模式
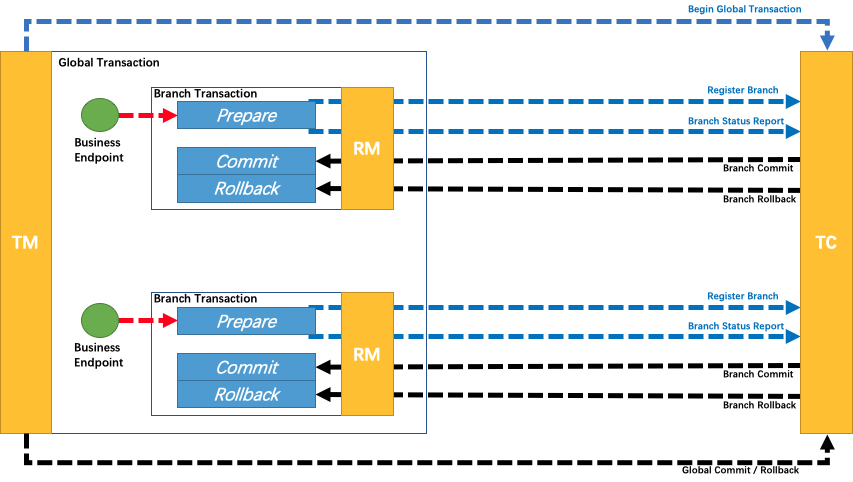
1、一阶段 prepare 行为:调用自定义的 prepare 逻辑;(比如插入订单,锁定库存,冻结部分余额)
2、二阶段 commit 行为: 调用自定义的 commit 逻辑;(减少库存、扣款)
3、二阶段 rollback 行为:调用自定义的 rollback 逻辑;(回滚订单、释放库存、解冻部分余额)
订单服务
//服务入口不需要try、commit、cancel,因为发生异常已立即回滚
@Override
@GlobalTransactional //seata全局事务注解
public String createOrder(Integer userId, Integer productId) {
Integer amount = 1; // 购买数量,暂时设为 1
log.info("[createOrder] 当前 XID: {}", RootContext.getXID());
// 减库存 (feign的调用) http远程调用
Store store = feignProductService.reduceStock(productId, amount);
// 减余额
feignAccountService.reduceBalance(userId, store.getPrice().toPlainString());
// 下订单
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(userId);
order.setProductId(productId);
order.setPayAmount(store.getPrice().multiply(new BigDecimal(amount)));
orderMapper.insertSelective(order);
log.info("[createOrder] 下订单: {}", order.getId());
// 返回订单编号
return String.valueOf(order.getId());
}
仓储服务
// TCC事务注解
@LocalTCC
public interface StoreService {
/**
* 锁定库存,try操作
*/
@TwoPhaseBusinessAction(
name = "reduceStock",
commitMethod = "commitTcc",
rollbackMethod = "cancelTcc")
Store reduceStock(@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = "productId") Integer productId,
@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = "amount") Integer amount);
/**
* 提交操作
*/
boolean commitTcc(BusinessActionContext context);
/**
* 取消操作
*/
boolean cancelTcc(BusinessActionContext context);
}
/* ################################################################################################# */
@Slf4j
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class StoreServiceImpl implements StoreService {
private final StoreTccMapper storeMapper;
private final TccStatusMapper tccStatusMapper;
@Override
@Transactional
public Store reduceStock(Integer productId, Integer amount) {
log.info("[reduceBalance] 当前 XID: {}", RootContext.getXID());
// 幂等,如果xid重复 主键冲突
// 防悬挂控制(cancel 比 try先执行),cancel已经插入记录,主键冲突
TccStatus tccStatus = new TccStatus();
tccStatus.setTryStatus(true);
tccStatus.setXid(RootContext.getXID());
tccStatusMapper.insertSelective(tccStatus);
// 检查余额
Store store = storeMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(productId);
if (store.getStock().compareTo(amount) < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("库存不足");
}
// 执行冻结操作
int updateCount = storeMapper.lockStore(productId, amount);
if (updateCount == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("库存不足");
}
log.info("[reduceBalance] 锁定库存 {} 成功", productId);
return store;
}
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean commitTcc(BusinessActionContext context) {
log.info("Confirm阶段,AccountServiceImpl, commitTcc --> xid = {}", context.getXid() + ", commitTcc提交成功");
TccStatus tccStatusRecord = tccStatusMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(context.getXid());
// 解决幂等
if (tccStatusRecord == null || tccStatusRecord.getCommitStatus()) {
return true;
}
Integer productId = (Integer) context.getActionContext("productId");
Integer amount = (Integer) context.getActionContext("amount");
int updateCount = storeMapper.reduceStock(productId, amount);
tccStatusRecord.setCommitStatus(true);
tccStatusMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(tccStatusRecord);
return updateCount != 0;
}
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean cancelTcc(BusinessActionContext context) {
log.info("Cancel阶段,AccountServiceImpl, cancelTcc --> xid = " + context.getXid() + ", cancelTcc提交失败");
TccStatus tccStatusRecord = tccStatusMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(context.getXid());
// 空回滚
if (tccStatusRecord == null ) {
TccStatus tccStatus = new TccStatus();
tccStatus.setXid(context.getXid());
tccStatus.setCancelStatus(true);
return true;
}
// 解决幂等
if (tccStatusRecord.getCancelStatus()) {
return true;
}
//进行数据库回滚处理
Integer productId = (Integer) context.getActionContext("productId");
Integer amount = (Integer) context.getActionContext("amount");
//把余额再加回去
storeMapper.increaseStock(productId, amount);
tccStatusRecord.setCancelStatus(true);
int updateCount = tccStatusMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(tccStatusRecord);
log.info("Cancel阶段,AccountServiceImpl, cancelTcc this data: productId= {}, amount = {}", productId, amount);
return updateCount != 0;
}
}
账户服务
@LocalTCC
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 扣除余额总方法,当前相当于try,为锁定部分余额
* 定义两阶段提交
* name = reduceStock为一阶段try方法
* commitMethod = commitTcc 为二阶段确认方法
* rollbackMethod = cancel 为二阶段取消方法
* BusinessActionContextParameter注解 可传递参数到二阶段方法
*
* @param userId 用户ID
* @param money 扣减金额
* @throws Exception 失败时抛出异常
*/
@TwoPhaseBusinessAction(
name = "reduceBalance",
commitMethod = "commitTcc",
rollbackMethod = "cancelTcc")
void reduceBalance(@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = "userId") Integer userId,
@BusinessActionContextParameter(paramName = "money") BigDecimal money);
/**
* 确认方法、可以另命名,但要保证与commitMethod一致
* context可以传递try方法的参数
*
* @param context 上下文
* @return boolean
*/
boolean commitTcc(BusinessActionContext context);
/**
* 二阶段取消方法
*
* @param context 上下文
* @return boolean
*/
boolean cancelTcc(BusinessActionContext context);
}
/* ################################################################################################# */
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private final AccountTccMapper accountMapper;
private final TccStatusMapper tccStatusMapper;
@Override
@Transactional
public void reduceBalance(Integer userId, BigDecimal money) {
log.info("[reduceBalance] 当前 XID: {}", RootContext.getXID());
// 幂等,如果xid重复 主键冲突
// 防悬挂控制(cancel 比 try先执行),cancel已经插入记录,主键冲突
TccStatus tccStatus = new TccStatus();
tccStatus.setTryStatus(true);
tccStatus.setXid(RootContext.getXID());
tccStatusMapper.insertSelective(tccStatus);
// 检查余额
Account account = accountMapper.selectAccountByUserId(userId);
if (account.getBalance().compareTo(money) < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足");
}
// 执行冻结操作
int updateCount = accountMapper.lockBalance(userId, money);
if (updateCount == 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足");
}
log.info("[reduceBalance] 锁定用户 {} 余额成功", userId);
}
/**
* tcc服务(confirm)方法
* 可以空确认
*/
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean commitTcc(BusinessActionContext context) {
log.info("Confirm阶段,AccountServiceImpl, commitTcc --> xid = {}", context.getXid() + ", commitTcc提交成功");
TccStatus tccStatusRecord = tccStatusMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(context.getXid());
// 解决幂等
if (tccStatusRecord == null || tccStatusRecord.getCommitStatus()) {
return true;
}
Integer userId = (Integer) context.getActionContext("userId");
BigDecimal money = (BigDecimal) context.getActionContext("money");
int updateCount = accountMapper.reduceBalance(userId, money);
tccStatusRecord.setCommitStatus(true);
tccStatusMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(tccStatusRecord);
return updateCount != 0;
}
/**
* tcc服务(cancel)方法
*
* @param context 上下文
* @return boolean
*/
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean cancelTcc(BusinessActionContext context) {
log.info("Cancel阶段,AccountServiceImpl, cancelTcc --> xid = " + context.getXid() + ", cancelTcc提交失败");
TccStatus tccStatusRecord = tccStatusMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(context.getXid());
// 空回滚
if (tccStatusRecord == null ) {
TccStatus tccStatus = new TccStatus();
tccStatus.setXid(context.getXid());
tccStatus.setCancelStatus(true);
return true;
}
// 解决幂等
if (tccStatusRecord.getCancelStatus()) {
return true;
}
//进行数据库回滚处理
Integer userId = (Integer) context.getActionContext("userId");
BigDecimal money = (BigDecimal) context.getActionContext("money");
//把余额再加回去
accountMapper.increaseBalance(userId, money);
tccStatusRecord.setCancelStatus(true);
int updateCount = tccStatusMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(tccStatusRecord);
log.info("Cancel阶段,AccountServiceImpl, cancelTcc this data: userId= {}, money = {}", userId, money);
return updateCount != 0;
}
}
四、Seata集群部署
在生产环境下,需要部署集群Seata TC Server实现高可用,在集群时多个Seata TC Server通过数据库或者redis实现全局事务会话信息的共享。每个Seata TC Server注册自己到注册中心上,应用从注册中心获得Seata TC Server实例,这就是Seata TC Server的集群
搭建步骤:
第一步:在源码目录下seata/script/server/db/mysql.sql有需要执行的脚本
第二步:修改seata/conf/file.conf配置文件,修改使用数据库,实现Seata TC Server的全局事务会话信息的共享
store {
mode = "db"
db {
datasource = "druid".
dbType = "mysql"
driverClassName = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"
url = "jdbc:mysql://192.168.22.1/seata?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai"
user = "root"
password = "123456"
minConn = 5
maxConn = 100
globalTable = "global_table"
branchTable = "branch_table"
lockTable = "lock_table"
queryLimit = 100
}
第三步:修改seata/conf/registry.conf配置文件,设置使用Nacos注册中心
registry {
type = "nacos"
loadBalance = "RandomLoadBalance"
loadBalanceVirtualNodes = 10
nacos {
# 为Nacos注册的服务名,1.4版本和Spring Cloud对接时发现serviceName被写死了为serverAddr,所以必须为此值
application = "serverAddr"
serverAddr = "192.168.22.1:8848"
# 为Nacos注册的组名,1.4版本和Spring Cloud对接时发现group被写死了为DEFAULT_GROUP,所以必须为此值
group = "DEFAULT_GROUP"
namespace = "DEV"
# 为Nacos注册的集群名,与spring cloud配置的虚拟组和分组的映射有关
cluster = "SEATA"
# 不需要用户名和密码
username = ""
password = ""
}
# 如果配置文件在Nacos需要将type = "nacos",一般情况使用的是file.conf则为file
config {
type = "nacos"
nacos {
serverAddr = "192.168.22.1:8848"
namespace = "DEV"
group = "DEFAULT_GROUP"
username = ""
password = ""
}
}
}
第三步:启动Seata TC Server,可能需要修改启动脚本中JVM参数【默认2G】
代码中的YAML修改:
seata:
# Seata应用编号,默认为${spring.application.name}
application-id: seata-at-store-service
enabled: true
# 注册中心
registry:
type: nacos
nacos:
cluster: SEATA
server-addr: localhost
namespace: DEV
# Seata事务组编号,用于TC集群名,一般用${spring.application.name}-group
tx-service-group: 'seata-at-store-service-group'
# 虚拟组和分组的映射
service:
vgroup-mapping:
# 此配置需要和seata中register文件的cluster一致
seata-at-store-service-group: 'SEATA'